Running spark lama app on Spark YARN
Next, it will be shown how to run the examples/spark/tabular-preset-automl.py script for execution on local Hadoop YARN.
Local deployment of Hadoop YARN is done using the docker-hadoop project from the https://github.com/big-data-europe/docker-hadoop repository. It consists of the following services: datanode, historyserver, namenode, nodemanager, resourcemanager. The files docker-hadoop/nodemanager/Dockerfile, docker-hadoop/docker-compose.yml have been modified and a description of the new service docker-hadoop/spark-submit has been added. Required tools to get started to work with docker-hadoop project: Docker, Docker Compose and GNU Make.
1. First, let’s go to the LightAutoML project directory
Make sure that in the dist directory there is a wheel assembly and in the jars directory there is a jar file.
If the dist directory does not exist, or if there are no files in it, then you need to build lama dist files.
./bin/slamactl.sh build-lama-dist
If there are no jar file(s) in jars directory, then you need to build lama jar file(s).
./bin/slamactl.sh build-jars
2. Distribute lama wheel to nodemanager
Copy lama wheel file from dist/LightAutoML-0.3.0-py3-none-any.whl to docker-hadoop/nodemanager/LightAutoML-0.3.0-py3-none-any.whl.
We copy the lama wheel assembly to the nodemanager Docker file, because later it will be needed in the nodemanager service to execute the pipelines that we will send to spark.
cp dist/LightAutoML-0.3.0-py3-none-any.whl docker-hadoop/nodemanager/LightAutoML-0.3.0-py3-none-any.whl
3. Go to docker-hadoop directory
cd docker-hadoop
4. Open docker-compose.yml file and configure services.
nano docker-compose.yml
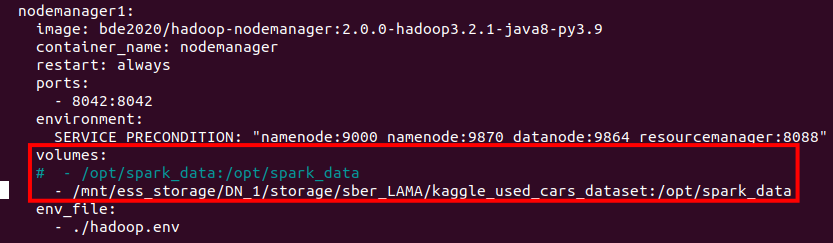
Edit volumes setting to mount directory with datasets to nodemanager service.
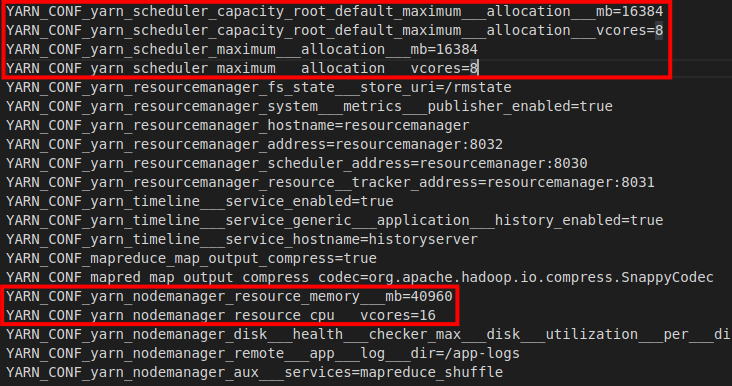
5. Open hadoop.env file and configure hadoop settings.
Pay attention to the highlighted settings. They need to be set in accordance with the resources of your computers.
6. Build image for nodemanager service.
The following command will build the nodemanager image according to docker-hadoop/nodemanager/Dockerfile. Python 3.9 and the installation of the lama wheel package has been added to this Dockerfile.
make build-nodemanager-with-python
7. Build image for spark-submit service.
The spark-submit container will be used to submit our applications for execution.
make build-image-to-spark-submit
8. Start Hadoop YARN services
docker-compose up
or same in detached mode:
docker-compose up -d
Check that all services have started:
docker-compose ps
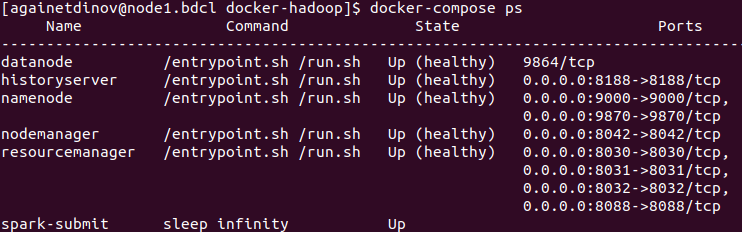
Here datanode, historyserver, namenode, nodemanager, resourcemanager is services of Hadoop. namenode and datanode is parts of HDFS. resourcemanager, nodemanager and historyserver is parts of YARN. For more information see the documentation at https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r1.2.1/hdfs_design.html and https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/stable/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html.
spark-submit is service to submitting our applications to Hadoop YARN for execution (see step 9).
If one of the services did not up, then you need to look at its logs. For example resourcemanager logs.
docker-compose logs -f resourcemanager
9. Send job to cluster via spark-submit container
docker exec -ti spark-submit bash -c "./bin/slamactl.sh submit-job-yarn dist/LightAutoML-0.3.0.tar.gz,examples/spark/examples_utils.py examples/spark/tabular-preset-automl.py"
10. Monitoring application execution
To monitor application execution, you can use the hadoop web interface (http://localhost:8088), which displays the status of the application, resources and application logs.
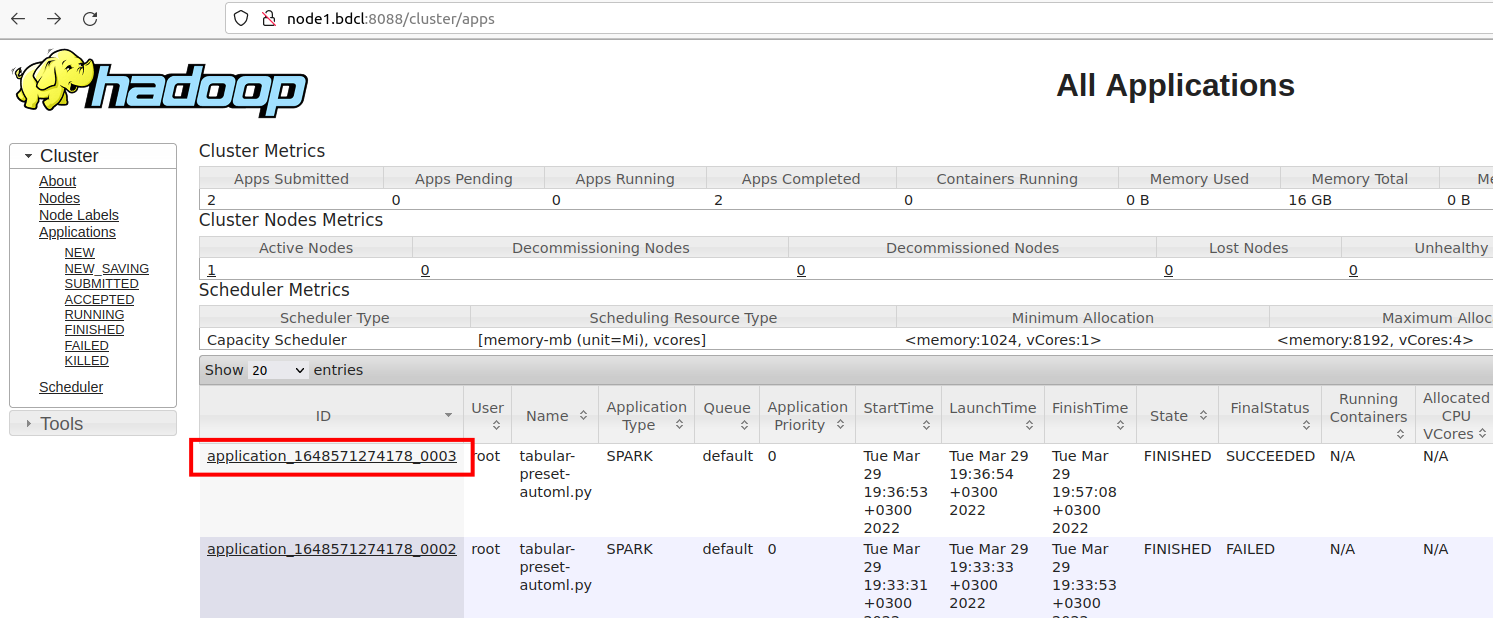
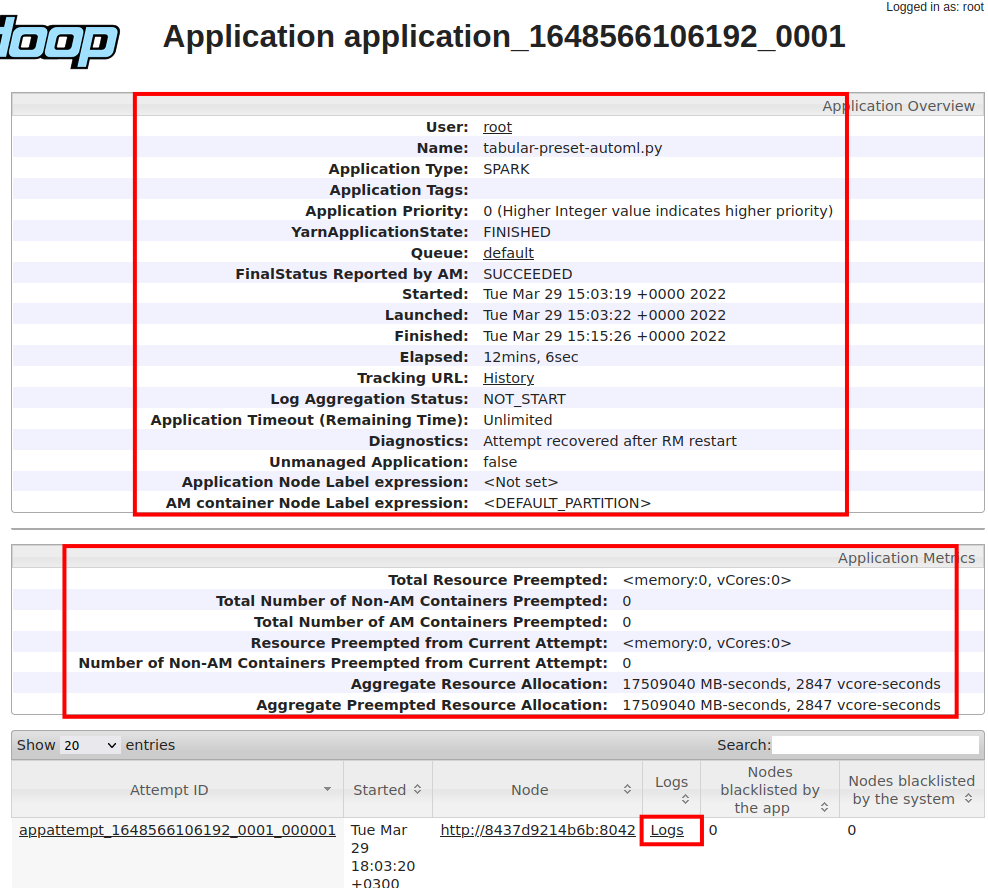
Let’s see the information about the application and its logs.
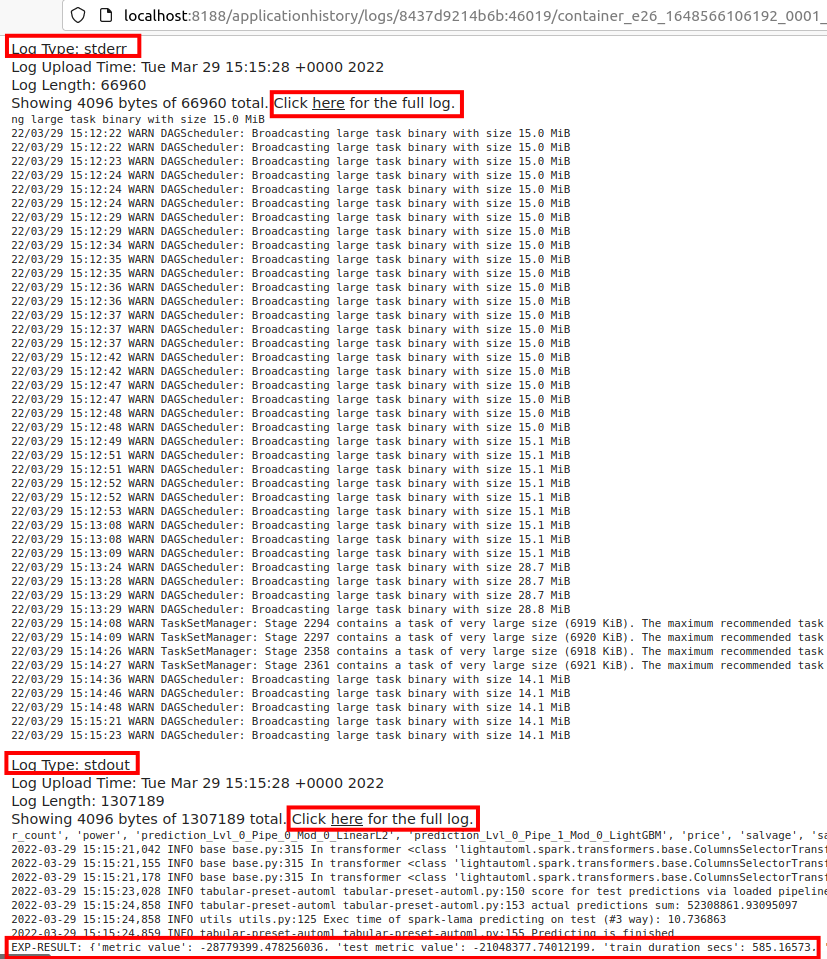
11. Spark WebUI
When the application is running, you can go to the hadoop web interface and get a link to the Spark WebUI.
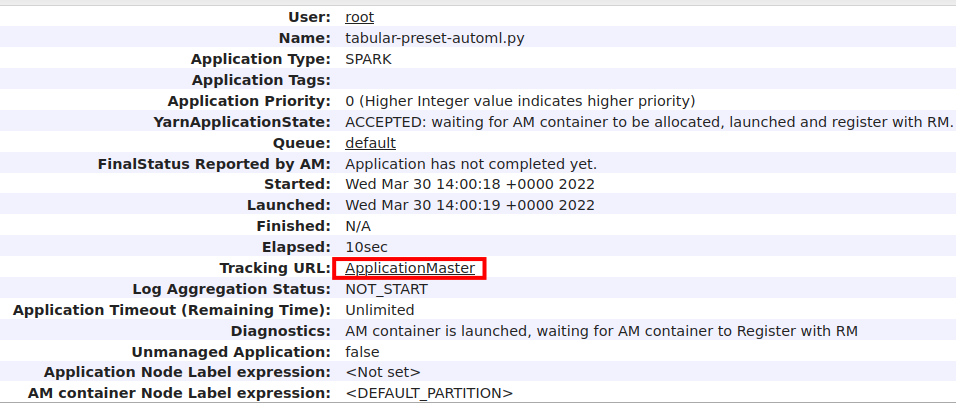
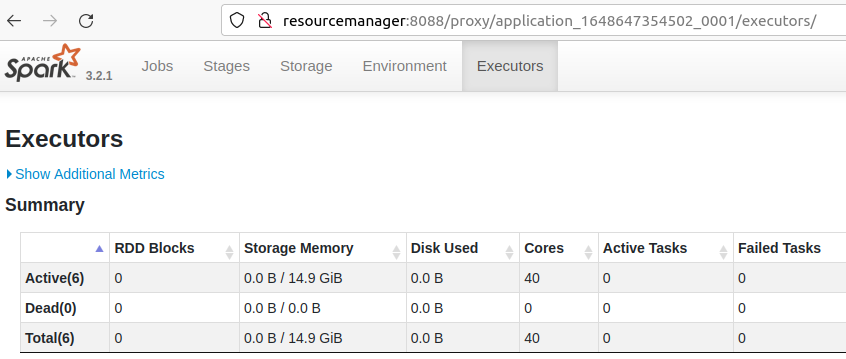
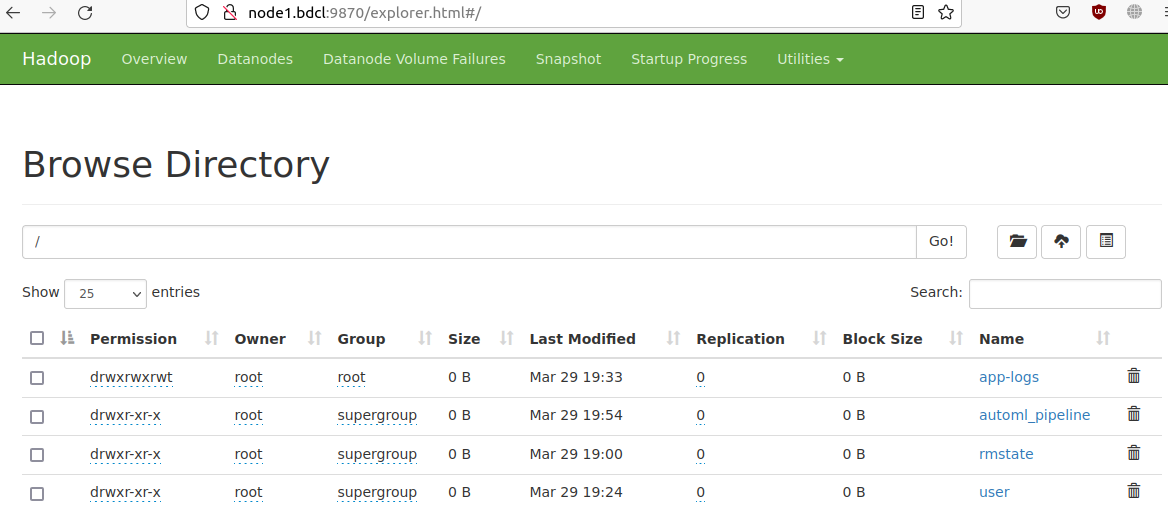
12. HDFS Web UI
HDFS Web UI is available at http://localhost:9870. Here you can browse your files in HDFS http://localhost:9870/explorer.html. HDFS stores trained pipelines and Spark application files.